-

Syphilis is at its highest levels since the 1950s. Here's how experts are trying to fix that.
Doctors and public health workers across the U.S. are racing to develop innovative and unconventional strategies to test and treat people for the infection.
-

Their loved ones died after receiving pig organ transplants. The families have no regrets.
Four people have received hearts or kidneys from pigs. Some of their relatives recount a roller coaster of hope and uncertainty.
-

Some types of HPV may affect men's fertility, new study suggests
Scientists have long considered that the world’s most common sexually transmitted infection, human papillomavirus, or HPV, may be a driver of infertility.
-

What is mpox?
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a virus first discovered in 1958 that causes fever, headache, muscle aches and exhaustion and eventually painful, fluid-filled blisters, or “pox,” over the body.
-

15-year-old Virginia scientist created a soap that could treat skin cancer, named Time's 2024 Kid of the Year
Bekele, from Fairfax, Virginia, is being recognized for developing an affordable bar of soap that could make delivering medications for skin cancers, including melanoma, more accessible.
-

What you need to know about ketamine
Ketamine is a prescription medication which is also abused recreationally under the street names Special K, Super K and Vitamin K. Here’s what you need to know.
-

FDA approves new blood test to screen for colon cancer
A blood test to screen for colon cancer was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Monday. It’s from Guardant Health and it’s called Shield.
-

Infants' tongue-tie may be overdiagnosed and needlessly treated, American Academy of Pediatrics says
A prominent doctors’ group worries that a condition in infants that can affect breastfeeding known as tongue-tie is being overdiagnosed in the U.S. and too often treated with unnecessary surgery.
-

Blood tests for Alzheimer's may be coming to your doctor's office. Here's what to know
New research suggests certain blood tests could help doctors diagnose Alzheimer’s disease faster and more accurately.
-
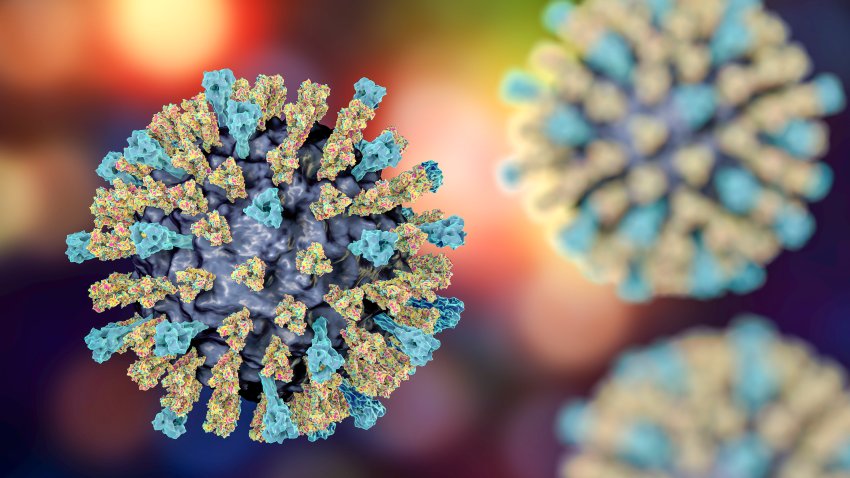
What is measles?
Measles is a highly contagious airborne disease caused by a virus that can lead to severe complications and death.
-

Experts say a twice-yearly injection that offers 100% protection against HIV is ‘stunning'
A study shows that a twice-yearly shot was 100% effective in preventing new HIV infections in women in Africa. The shot is already used in the U.S. and elsewhere as a treatment for the virus that causes AIDS, and drugmaker Gilead is testing it for prevention.
-

Scientists say they have identified a root cause of lupus — one that could pave the way for new treatments
A study published Wednesday in the journal Nature outlines a clear pathway for how the disease likely develops, pointing to abnormalities in the immune systems of people with lupus.
-

What cognitive tests can show — and what they can't
President Joe Biden is under pressure to undergo cognitive testing even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam. But what can the brief screening tool actually tell about a person’s brain health? And when does the average older adult need one?
-

FDA approves a second Alzheimer's drug that can modestly slow disease
U.S. health officials have approved a new Alzheimer’s drug that can modestly slow the disease.
-

Getting rid of poison ivy is a serious matter. What you should and shouldn't do
Poison ivy poses a serious problem for many who come into contact with it. What you should and shouldn’t do.
-

Beyond Ozempic: New GLP-1 drugs promise weight loss and health benefits
Researchers at the American Diabetes Association conference in Orlando are expected to present data on 27 GLP-1 drugs in development. Others target a different hormone.
-

Coffee habits are partly linked to genetics, UC San Diego researchers say
Researchers from UC San Diego found that some people are genetically predisposed to drink more coffee than others.
-
LA County health officials warn of bacteria levels at some beaches. See the list
The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health is cautioning residents looking for relief from early summer heat to avoid several beaches after finding bacteria levels exceeding health standards.
-

LA officials warn of beach bacteria as heat rises
The LA Department of Public Health recommends visitors avoid certain beaches due to excess bacteria. John Cádiz Klemack reports for Today in LA on Thursday, June 20, 2024.
-

Mpox cases spike in Los Angeles County
The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health reported today a “concerning increase” of 10 new cases of mpox in the past two weeks, up from a countywide average of less than two cases per week the preceding several weeks.


